Bridge Ion Separation Technology™
BIST™ provides an additional separation tool to a whole class of organic and inorganic charged molecules. BIST™ columns, simple mobile phases, and an array of applications provide a whole new continent on the chromatography map.
Read more about A New Mode of LC Separation
Analyze Ions Differently
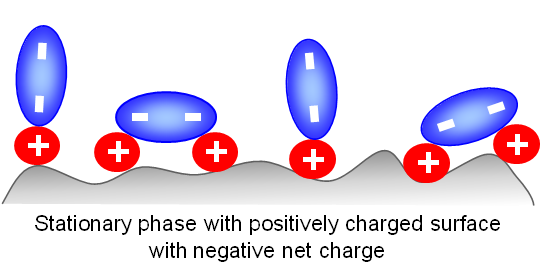
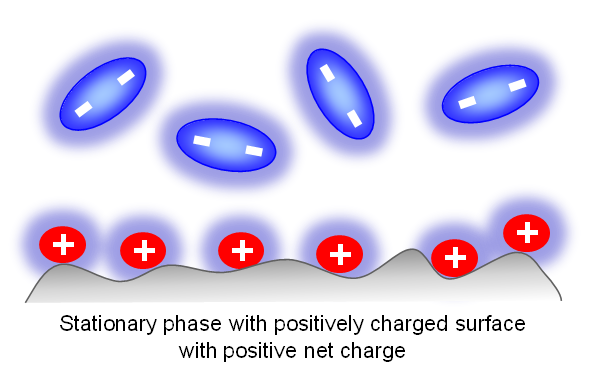
When doubly-charged ions are present in the mobile phase (MP), the surface of the stationary phase can switch its polarity.
For example: if the surface is positively-charged and the doubly-charged ions in the mobile phase are sulfate ions with a minus 2 charge (from ionized sulfuric acid), then the surface become negatively-charged.
However, this can occur only when the mobile phase has a relatively low concentration of water. When water is the main component of the mobile phase, it forms a solvation shell around each ion and prevents the surface charge from switching.
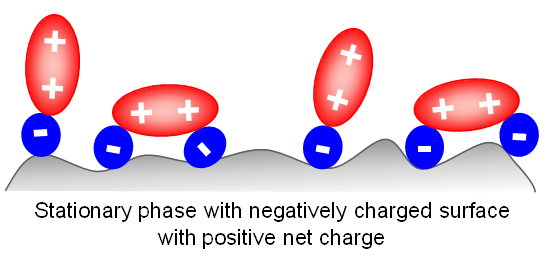
The same surface switch is observed when a negatively-charged surface interacts with doubly-charged positive ions such as diamines, and some inorganic ions such as Mg2+ and Ca2+.